The Bank of England’s base rate is one of the most significant financial benchmarks in the UK economy.
It affects everything from mortgage repayments to savings account interest, and any change in the rate can have wide-reaching consequences.
For homeowners, savers, and investors alike, understanding when the next Bank of England base rate review will take place is key to staying ahead financially.
What Is The Current Bank Of England Base Rate?

As of the latest meeting on 19 June 2025, the Bank of England’s base rate is set at 4.25%. This figure represents the cost at which the Bank of England lends money to other banks.
The rate serves as a benchmark for the wider UK economy and influences both borrowing and saving.
This rate remains a key tool in monetary policy, helping to control inflation and ensure financial stability.
While 4.25% marks a relatively high level compared to rates in the past decade, it reflects ongoing efforts by the Bank to manage inflation and economic pressures.
When Will The Next Bank Of England Interest Rate Decision Take Place?
The next meeting of the Monetary Policy Committee is scheduled for 7 August 2025. These meetings are pre-planned and occur approximately every six weeks. During each meeting, the committee reviews:
- The current state of the UK economy
- Domestic and international financial trends
- Inflation targets and projections
- Employment levels and consumer spending
Although changes to the base rate are not guaranteed at each meeting, any adjustments are widely anticipated and often influence markets, mortgage lenders, and savers.
How Often Does The Bank Of England Review The Base Rate?
The Monetary Policy Committee meets eight times a year to evaluate whether a change to the base rate is necessary.
These regular reviews follow a structured schedule, which is published annually on the Bank’s official website.
Emergency meetings can be called if there is significant economic instability or unexpected developments such as a financial crisis or severe inflation spikes. However, in most cases, decisions are made according to the standard timetable.
What Is The Base Rate And Why Does It Matter?

The Bank of England base rate is the official interest rate set by the central bank. It influences the rate at which commercial banks borrow money and directly impacts the rates consumers receive from financial institutions.
Key areas affected by the base rate include:
- Mortgage interest rates
- Personal and business loan rates
- Credit card interest
- Savings account returns
Higher base rates generally mean more expensive borrowing and better savings returns, while lower base rates reduce borrowing costs but diminish interest earned on savings.
How Do Changes In The Base Rate Impact Mortgages In The UK?
When the Bank of England adjusts the base rate, one of the most immediate and noticeable effects is on the UK mortgage market.
This is because most mortgage interest rates—whether variable or fixed—are either directly or indirectly influenced by the base rate. Changes can affect monthly repayments, borrowing costs, and the overall affordability of homes.
The type of mortgage a borrower holds plays a crucial role in determining how significantly a base rate adjustment will impact their financial situation.
Tracker Mortgages: Immediate and Direct Impact
Tracker mortgages are directly linked to the Bank of England base rate. These deals usually follow the base rate with an additional set percentage defined by the lender. For example, if a tracker mortgage is set at “base rate + 1.5%” and the base rate is 4.25%, the total interest charged will be 5.75%.
When the base rate increases:
- Borrowers will see a corresponding rise in their monthly mortgage payments
- Increases are often implemented within 30 days of the rate announcement
- The cost of borrowing rises in proportion to the base rate movement
When the base rate decreases:
- Monthly mortgage payments fall by the same proportion
- Borrowers benefit from immediate savings without needing to renegotiate terms
This makes tracker mortgages highly responsive but also unpredictable, which can lead to budgeting challenges during periods of rate volatility.
Fixed-Rate Mortgages: Stability During the Term, but Exposure Later
Fixed-rate mortgages provide borrowers with a locked-in interest rate for a set period, usually between two and five years. This means that:
- Monthly repayments remain consistent throughout the fixed term, offering financial stability
- Changes in the base rate during the fixed term have no impact on repayments
However, once the fixed period expires, borrowers are typically moved onto the lender’s standard variable rate (SVR), which may be significantly higher and more sensitive to base rate fluctuations.
At this point, borrowers could be exposed to higher costs, especially if the base rate has increased substantially since the original deal was secured.
To mitigate this, many homeowners begin shopping for new fixed deals during the final six months of their current term to avoid being automatically transferred to an SVR.
Standard Variable Rate (SVR) Mortgages: Indirect But Significant Impact
An SVR mortgage is one where the lender sets the interest rate and can change it at any time. While not directly tied to the base rate, SVRs usually respond to it because:
- Lenders use the base rate as a benchmark to assess their own borrowing costs
- Changes to the base rate influence how competitive lenders want to remain
When the base rate rises, SVRs often follow suit. However, lenders may choose to increase or decrease their SVRs based on a combination of factors, including market trends, risk appetite, and profit margins. This makes SVR mortgages somewhat unpredictable and potentially expensive over time.
Borrowers with SVR mortgages should stay informed about base rate announcements and be prepared to switch products if better rates become available.
Discount Rate Mortgages: Dependent on SVRs and Market Movement
Discount rate mortgages offer a set percentage discount off the lender’s SVR for a limited period. For example, a deal might offer a 1% discount off a 6% SVR, meaning the borrower pays 5% interest.
The implications of base rate changes are similar to those for SVR mortgages, since:
- The discounted rate still depends on the SVR, which may move up or down in response to base rate changes
- The borrower’s monthly payments will increase or decrease depending on how the lender reacts to the base rate shift
These products can offer initial savings, but like SVRs, they expose borrowers to variability and require close monitoring of interest rate trends.
Interest-Only Mortgages: Affects Repayment Planning
For borrowers on interest-only mortgages, base rate changes influence how much they pay in monthly interest.
Since they are not repaying the capital during the mortgage term, their exposure to interest rate fluctuations is more pronounced:
- An increase in the base rate raises interest-only payments, which can be financially burdensome
- A decrease reduces the payment, but the original loan amount remains unchanged
Interest-only borrowers must remain aware of how rising rates could significantly increase their financial obligations, especially as they approach the end of the term when the capital must be repaid.
Buy-To-Let Mortgages: Higher Sensitivity for Investors
Landlords with buy-to-let properties are often on interest-only or variable-rate mortgages. A rise in the base rate can:
- Increase monthly mortgage payments
- Reduce rental yield margins
- Potentially lead to higher rents if landlords pass on the cost to tenants
Investors in the buy-to-let market are particularly sensitive to base rate changes because profitability is closely tied to financing costs.
Summary Of Mortgage Types And Base Rate Sensitivity
| Mortgage Type | Linked To Base Rate? | Rate Flexibility | Impact Of Base Rate Changes |
| Tracker Mortgage | Yes | High | Immediate and equal change |
| Fixed-Rate Mortgage | No (during term) | None (during term) | Affects rate only after fixed term ends |
| Standard Variable Rate | Indirect | Medium | Adjusts at lender’s discretion |
| Discount Rate Mortgage | Indirect via SVR | Medium | Depends on lender’s SVR movement |
| Interest-Only Mortgage | Varies | High | Payment affected by rate change |
| Buy-To-Let Mortgage | Often variable | High | Significant impact on profitability |
Understanding how different mortgage products respond to base rate movements is essential for managing costs and making informed financial decisions.
Whether planning to remortgage, buy a property, or switch lenders, awareness of the current rate environment allows borrowers to make proactive choices and avoid unnecessary expense.
How Does The Base Rate Influence Borrowing And Saving In The UK?
The Bank of England base rate has a ripple effect across the financial landscape, shaping both borrowing and saving behaviours in the UK.
Understanding its influence helps individuals and businesses make more informed decisions.
Impact On Borrowing And Saving
| Financial Product | Effect Of Base Rate Increase | Effect Of Base Rate Decrease |
| Tracker Mortgages | Higher monthly payments | Lower monthly payments |
| Fixed-Rate Mortgages | No change during fixed term | No change during fixed term |
| Standard Variable | Likely to increase | Likely to decrease |
| Savings Accounts | Better returns | Lower interest earnings |
| Loans & Credit Cards | Increased borrowing costs | Reduced borrowing costs |
This influence is part of a wider monetary policy strategy aimed at either stimulating or cooling the economy, depending on the prevailing conditions.
What Economic Indicators Affect The Bank Of England’s Rate Decisions?
The Bank of England uses a range of economic indicators to decide whether to adjust the base rate. These include:
- Inflation: The Bank’s primary goal is to keep inflation at around 2%. Rising inflation often triggers rate increases to cool spending.
- GDP Growth: Strong economic growth may lead to higher rates to prevent overheating, while weak growth could encourage rate cuts.
- Employment Levels: High unemployment typically supports lower rates to stimulate job creation. Rising employment may lead to increased rates.
- Consumer Spending: Surges in spending can drive inflation, prompting the Bank to increase the base rate.
- Global Economic Events: International trends and geopolitical risks also influence the decision-making process.
Monitoring these indicators gives financial professionals insight into potential future changes in monetary policy.
Can You Predict Future Changes In The Base Rate?
Although exact rate changes cannot be predicted, analysts and economists often assess macroeconomic signals and Bank of England communications to anticipate direction.
Typical tools and sources for forecasting include:
- Official inflation reports and consumer price index data
- Public speeches by MPC members
- Minutes and voting results from previous MPC meetings
- Market sentiment and investor behaviour
- International trends in major economies such as the United States and European Union
These factors often provide early indicators of whether rates are likely to rise, fall or stay the same.
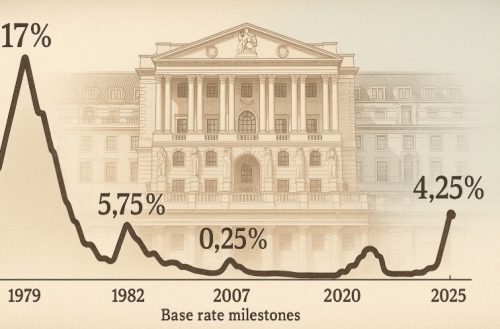
How Has The Bank Of England Base Rate Changed Over Time?

The base rate has shifted dramatically over the centuries in response to both local and global economic conditions. Key periods in the UK’s interest rate history highlight the flexibility of monetary policy.
Historical Highlights Of The UK Interest Rate
- Between 1719 and 1822, the base rate remained stable at 5%, later dropping to 4%
- In 1979, the rate peaked at 17% to combat inflation
- In March 2020, the rate hit a historic low of 0.1% during the COVID-19 crisis
Recent Trends Since 2020
The following table outlines base rate changes since 2020:
| Date | Base Rate (%) | Reason/Context |
| March 2020 | 0.10 | COVID-19 economic emergency |
| December 2021 | 0.25 | Inflation pressure begins |
| August 2022 | 1.75 | Continued rise in inflation |
| June 2023 | 4.50 | Aggressive tightening to control prices |
| June 2025 | 4.25 | Slight easing as inflation stabilises |
The base rate has been rising steadily in response to economic recovery and rising prices, although the Bank has recently shown signs of easing policy as inflation moderates.
Should Homeowners Fix Their Mortgage Rate Now?
With current uncertainty in the interest rate landscape, many homeowners are considering whether to lock in a fixed-rate deal now. Key points to consider include:
- Fixed-rate deals may be more expensive than those taken out in previous years, especially before 2022
- However, they may still be lower than future SVR increases if the base rate rises again
- Borrowers within six months of their current deal ending should explore new offers to avoid expensive rollovers
Mortgage brokers can assist in reviewing available products and securing competitive rates with enough time to act before term-end.
What Should You Do If You’re In The Process Of Switching Your Mortgage?
If you’re currently buying or remortgaging, flexibility is essential. Most lenders allow rate changes right up until the mortgage is completed, meaning:
- You can lock in a lower rate if market rates improve
- You are not bound until the transaction is finalised
- Early repayment charges may apply after completion if you choose to switch again
Speaking to a broker or adviser ensures you’re making decisions aligned with your financial goals and the latest market conditions.
Where Can You Get Expert Advice On Base Rate Changes?

Understanding how the base rate impacts your financial situation can be complex. To navigate this, you may want to consult:
- Mortgage brokers who compare rates across the market
- Financial advisers with expertise in rate forecasts
- Online calculators and planning tools offered by banks and comparison websites
Services such as Mojo Mortgages offer no-obligation consultations, helping homeowners and buyers assess their options and act before potential base rate changes take effect.
Conclusion
With the next base rate decision due on 7 August 2025, market participants are watching closely.
The BoE will weigh inflation, economic performance, and other key indicators before deciding whether to hold, raise, or cut the rate.
Staying informed about these meetings and understanding how changes affect your financial life is crucial, whether you’re managing a mortgage, loan, or savings plan.
FAQs
How do I find out when the Bank of England meets?
The Bank of England publishes its MPC meeting schedule for the full year on its official website.
Will interest rates rise again in 2025?
It’s uncertain, but economic forecasts and inflation trends suggest that modest increases are still possible, depending on market data.
How quickly do mortgage rates change after a base rate review?
Tracker mortgages adjust immediately, while SVR and new fixed-rate deals may follow within days or weeks after the announcement.
Can I fix my mortgage rate before my deal ends?
Yes, most lenders allow you to secure a new deal up to six months before your current one ends without penalties.
Are savings accounts better during high interest rate periods?
Yes, banks generally increase the interest offered on savings accounts when the base rate rises.
Do all lenders react the same way to base rate changes?
No, each lender interprets rate changes differently. Some pass on increases fully; others only partially.
How does inflation impact the Bank of England base rate?
Higher inflation often leads the BoE to increase the base rate to reduce spending and stabilise prices.




























